Introduction:
In today’s digital landscape, ensuring the optimal performance and availability of web applications is crucial for businesses to provide a seamless user experience. Synthetic monitoring plays a vital role in proactively identifying performance issues and ensuring reliable application delivery.
how to get synthetics monitoring to work in new relic, New Relic, a leading application performance monitoring (APM) platform, offers robust synthetic monitoring capabilities that allow organizations to simulate user interactions and monitor application health from various locations worldwide. This article aims to provide a detailed guide on how to implement synthetic monitoring effectively in New Relic.
Step 1: Setting up the New Relic Account:

- Create an account: Visit the New Relic website and sign up for a new account if you haven’t already. Choose the appropriate subscription plan based on your organization’s needs.
- Install New Relic agents: Install the necessary New Relic agents on your web servers or applications to collect performance data. This step is essential to correlate synthetic monitoring results with real user experiences.
Step 2: Creating Synthetic Monitors:
- Access Synthetic Monitoring: Log in to your New Relic account and navigate to the Synthetic Monitoring section.
- Define monitor locations: Choose the geographic locations from which you want to simulate user interactions. New Relic offers a wide range of locations globally to provide comprehensive monitoring coverage.

- Select monitor type: Determine the type of monitor that suits your requirements. New Relic supports HTTP/S monitors, scripted browser monitors, and API monitors. HTTP/S monitors are ideal for simple checks, while scripted browser monitors allow for more complex interactions, such as logging in and form submissions. API monitors are used for testing RESTful APIs.
- Configure monitor settings: Provide the necessary details, such as URL, request headers, authentication credentials, etc., based on the monitor type you selected. Specify the expected behavior and response codes to define success or failure criteria.
- Set monitor frequency: Determine the frequency at which the synthetic monitor should run. New Relic allows you to choose the interval between tests, ensuring regular monitoring of your application’s availability and performance.
Step 3: Analyzing Synthetic Monitoring Results:
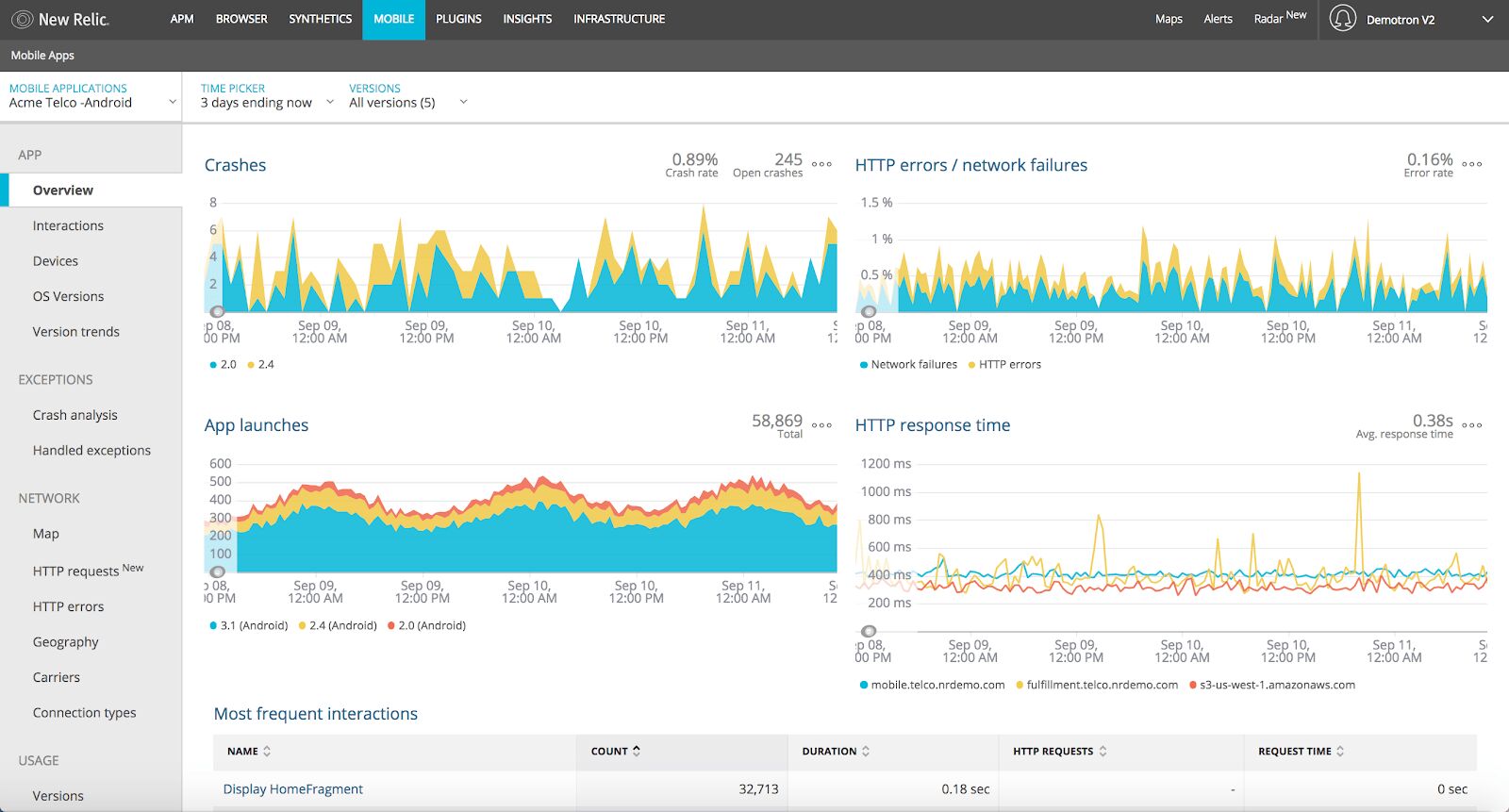
- View monitor results: Access the Synthetic Monitoring section in your New Relic account to view the results of your monitors. The dashboard provides an overview of the monitor status, response times, and errors.
- Analyze performance data: Dive deeper into the performance data to identify potential bottlenecks or issues. New Relic offers various visualizations and analytics tools to gain insights into response times, latency, throughput, and other key metrics.
- Set up alerts: Configure alerts to receive notifications when synthetic monitors fail or breach predefined thresholds. Alerts can be sent via email, SMS, or integrated with third-party collaboration tools like Slack or PagerDuty.
Step 4: Leveraging Advanced Features:

- Implement multi-step transactions: For complex web applications, use scripted browser monitors to simulate user workflows involving multiple steps. This helps uncover issues related to login processes, form submissions, or shopping cart interactions.
- Utilize global locations: New Relic allows you to monitor your application’s performance from various geographic locations. Leverage this feature to assess how user experiences differ based on their geographical location.
- Monitor third-party dependencies: Identify performance bottlenecks caused by third-party services or APIs by incorporating external service checks within your synthetic monitors. This ensures comprehensive monitoring of your application’s entire ecosystem.
Must Read=“24.5”” hp 25mx” | Full HD 144Hz Black
Conclusion:
how to get synthetics monitoring to work in new relic, Synthetic monitoring in New Relic empowers organizations to proactively detect and resolve application performance issues, ensuring an optimal user experience. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can successfully implement synthetic monitoring in New Relic, gain valuable insights into your application’s health, and take proactive measures to deliver exceptional performance. Continuously monitoring your application’s availability and responsiveness is crucial for staying ahead in today’s competitive digital landscape.
FAQS
Q1: What is synthetic monitoring?
A1: Synthetic monitoring is a technique used to simulate user interactions with a web application. It involves creating scripts or tests that mimic user actions, such as clicking buttons, filling out forms, and navigating through pages. Synthetic monitors run at regular intervals and provide insights into the availability, performance, and functionality of the application from various locations.
Q2: Why is synthetic monitoring important?
A2: Synthetic monitoring helps organizations proactively identify and address performance issues before they impact real users. By simulating user interactions, it provides a holistic view of the application’s health, detects bottlenecks, and measures response times. Synthetic monitoring enables businesses to optimize their web applications, deliver a seamless user experience, and maintain customer satisfaction.
Q3: How does New Relic’s synthetic monitoring work?
A3: New Relic’s synthetic monitoring allows you to create and schedule tests that simulate user interactions with your application. These tests are performed from New Relic’s global monitoring locations, and the results are collected and analyzed. New Relic provides detailed reports, dashboards, and alerting mechanisms to help you monitor the performance and availability of your application.
Q4: What types of monitors are available in New Relic?
A4: New Relic offers three types of monitors:
- HTTP/S monitors: These monitors check the availability and response times of web endpoints.
- Scripted browser monitors: These monitors simulate user interactions by navigating through pages, filling out forms, and performing complex actions.
- API monitors: These monitors validate the availability and response times of RESTful APIs.
Q5: Can I customize the frequency of synthetic monitors in New Relic?
A5: Yes, New Relic allows you to configure the frequency of synthetic monitors based on your needs. You can set the interval between tests to monitor your application’s availability and performance at desired intervals, such as every minute, five minutes, or even less frequently.